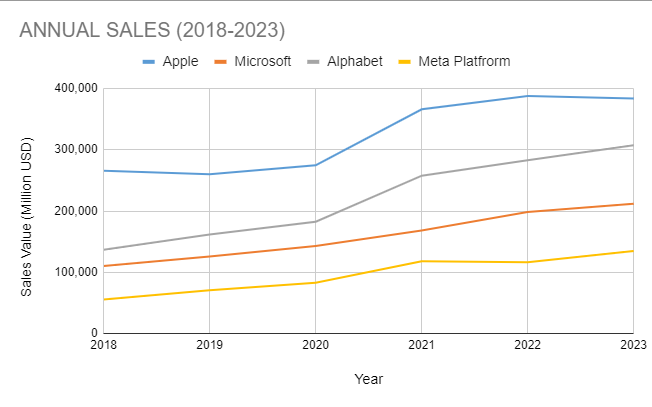
The global COVID-19 epidemic caused profound shifts in consumer behavior and market dynamics, which resulted in a notable increase in the sale of electronic products. The need for technological goods surged as the globe struggled with lockdowns, social isolation, and the move to remote employment and education. The article examines the causes of this upsurge, how it affected international supply networks and marketplaces, and its wider ramifications for the future. A comparison of Annual sales revenue of the top four electronics companies in the world is illustrated below for easy reference.
Electronics sales growth 2018-2023
Factors Driving the Surge in Electronic Appliances Purchasing
The abrupt and broad transition to remote work and online schooling was one of the main causes of the surge in the purchase of electronic appliances both during and after the pandemic. Now that millions are compelled to work from home, setting up home offices is becoming critically important. To accommodate many users, households that had previously relied on shared or limited gadgets now needed more appliances. The need for laptops, desktop computers, monitors, printers, and other office-related electronic appliances increased dramatically.

In a similar vein, the necessity for educational resources at home arose from the closing of schools and the switch to online instruction. To guarantee their children had access to online courses and educational resources, parents made investments in laptops, iPads, and other digital gadgets. Longer hours spent at home also led to a rise in the market for products related to comfort and home entertainment. Smart home gadgets, culinary appliances, game consoles, and televisions became necessities as individuals looked for ways to improve the usability and enjoyment of their living areas during lockdowns.
The increase in house improvement and renovation initiatives during the pandemic was another important element. Since more people were spending time at home, they decided to modernize their living areas, which resulted in a rise in the sales of household goods including air conditioners, refrigerators, and washing machines. Another factor was consumer desire for smart and energy-efficient appliances as they looked to upgrade their homes with the newest technologies.
Effects on Global Markets and Supply Chains
Supply chains and international marketplaces were significantly impacted by the spike in demand for electrical products. Production delays and shortages of supplies resulted from the pandemic's interruptions and the unexpected rise in consumer demand. Factories and manufacturing facilities had to deal with issues like a lack of workers, operational limitations, and trouble obtaining raw materials. This led to supply chain bottlenecks, which extended product lead times and, in certain situations, raised prices significantly.
These difficulties were made worse by the lack of semiconductors, which became apparent during the epidemic as a crucial problem. Numerous electronic equipment depend on semiconductors, and their scarcity caused production problems for a wide range of goods, including computers, smartphones, and home appliances. Businesses were compelled to focus on producing high-demand goods first, which resulted in a shortage of others. The mismatch between supply and demand heightened rivalry for the few products available and brought attention to the weaknesses in international supply chains.
Additionally, the increase in appliance purchases added to environmental worries, especially with relation to electronic trash (e-waste). E-waste increased significantly as a result of the increasing turnover of electronic appliances, which was caused by the necessity to replace outdated models as well as the desire for better technology. Due to a lack of appropriate recycling facilities, many consumers disposed of old appliances improperly, which resulted in the buildup of hazardous materials in landfills. This problem emphasizes the necessity of stricter recycling laws and policies to control the environmental effects of rising electronics use.
Implications for the Future
The post-pandemic spike in the purchase of electronic appliances has a number of long-term effects for the environment and the economy. Economic growth has been fueled by rising demand, which has led to investments in innovation and product line expansions by businesses catering to customer demands in the technology and home appliance sectors. This trend is anticipated to continue as customers value home comfort and convenience and remote work and online learning continue to be common.
Nonetheless, there are a lot of obstacles because of the environmental effects. The necessity for sustainable methods in the manufacture, usage, and disposal of electronic products is highlighted by the increase in e-waste. To create and administer efficient recycling programs, support the use of eco-friendly materials, and persuade customers to make more sustainable shopping decisions, governments and industry partners must work together. Furthermore, the energy required for the manufacture and upkeep of electronic goods adds to carbon emissions worldwide, highlighting the significance of renewable energy sources and energy-efficient technologies.
Global purchases of electronic appliances have increased since the pandemic, which is indicative of significant changes in consumer behavior and market dynamics as a result of COVID-19. This boom has accelerated technical development and economic expansion, but it has also exposed supply chain weaknesses and sparked serious environmental concerns. To secure a resilient and balanced future, it will be essential to address these issues via innovation, sustainability, and responsible consumption as the world continues to traverse the post-pandemic landscape.



 Never miss a story from us, get weekly updates in your inbox.
Never miss a story from us, get weekly updates in your inbox.