Risk is a constant factor in the intricate and dynamic field of supply chain management that greatly impacts operations, expenses, and overall company success. Supply chain managers use various tools and techniques, such as risk matrices and calculators, to efficiently manage these risks. This topic covers supply chain risk management strategies, a risk matrix, and the elements and uses of a supply chain risk calculator formula.
SUPPLY CHAIN RISK CALCULATION FORMULA
One quantitative technique for evaluating and quantifying possible hazards in a supply chain is the supply chain risk calculator formula. The principal aim is to assess the probability of diverse risk occurrences and their possible consequences to obtain an all-encompassing risk score. Making educated decisions about risk mitigation and risk prioritization is aided by this score.
The basic formula for calculating risk in the supply chain is:
Risk Score=∑(Probability of Event×Impact of Event×Weight of Event)
Where:
- Probability of Event (P)
- Impact of Event (I)
- Weight of Event (W
Below are the steps for calculating the Risk Score
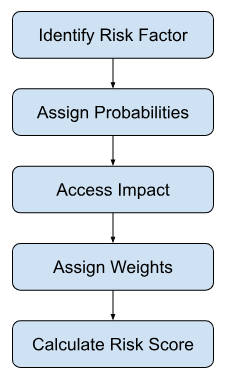
Let us take a case scenario for easy understanding:
A Supply Chain Manager evaluates the following risks to find the risk score.
| Risk factor | Supplier failure | Transportation delay | Natural disaster |
| Probability (%) | 30% | 40% | 10% |
| Impact (USD) | 200,000 | 150,000 | 1,000,000 |
| Weight | 0.3 | 0.5 | 0.2 |
| Risk Score | 18,000 | 30,000 | 20,000 |
| Total Risk Score | 68,000 |
This quantified risk score provides a clear and objective measure of the overall risk level, aiding in risk prioritization and management.
THE RISK MATRIX
By mapping risks according to their probability and impact, a risk matrix serves as an additional visual aid to the risk calculator. It offers a simple graphic representation that facilitates the rapid identification of risks that require immediate action and those that may be monitored over time.
The matrix is typically a grid with probability on one axis and impact on the other, divided into categories such as low, medium, and high. Each risk is placed within this grid based on its assessed probability and impact:
| Impact: Low | Impact: Medium | Impact: High | |
| Probability: High | Moderate Risk | High Risk | Critical Risk |
| Probability: Medium | Low Risk | Moderate Risk | High Risk |
| Probability: Low | Minimal Risk | Low Risk | Moderate Risk |
OVERCOMING SUPPLY CHAIN RISKS
In order to mitigate supply chain risks, a proactive, multifaceted strategy is needed. Here are a few tactics:
Diversification:
Supplier diversification: Sourcing from multiple suppliers, instead of depending on a single supplier to mitigate the risk of supplier failure.
Geographical Diversification: Spreading production and storage facilities across several regions to reduce the impacts of regional interruptions
Technology Integration:
Real-Time tracking: Using GPS monitoring and Internet of Things devices to keep an eye on shipments in real-time and react fast to any delays or disruptions.
Predictive analytics is the use of AI and big data to identify possible problems and create preventative measures.
Robust Contracts and Agreements:
Service Level Agreements (SLAs): To guarantee accountability and define standards for performance and response times, suppliers and logistics providers should establish explicit SLAs.
Insurance: Obtaining extensive insurance protection to guard against large monetary losses resulting from a variety of risk situations.
Inventory Management:
Safety Stock: Keeping an emergency supply on hand to cushion the effects of disruptions in the supply chain.
Demand Forecasting: Making more accurate forecasts about demand and modifying inventory levels in response by employing sophisticated forecasting technologies.
Regular Risk Assessment:
Identifying new risks and assessing the efficiency of current mitigation solutions through regular risk assessments.
Updating risk management strategies in response to new threats and shifting circumstances.
Collaboration and Communication:
Establishing effective lines of communication with every supply chain partner to guarantee prompt information exchange and well-coordinated disruption responses.
Collaborating on planning with logistics companies and suppliers to improve the overall resilience of the supply chain.
Supply chain operations that aim to effectively manage risk must incorporate strong tools such as the risk calculator and risk matrix. By offering an organized method for measuring and displaying risks, these tools help users make well-informed decisions. The proactive steps done to reduce these risks, however, are where a risk management approach shines. Supply chain managers may lessen the impact of possible disruptions by managing inventories effectively, utilizing technology, diversifying their suppliers, creating robust contracts, regularly doing risk assessments, and encouraging teamwork. This all-encompassing strategy not only makes supply chains more resilient, but also guarantees continued economic success in a world where uncertainty is growing.



 Never miss a story from us, get weekly updates in your inbox.
Never miss a story from us, get weekly updates in your inbox.